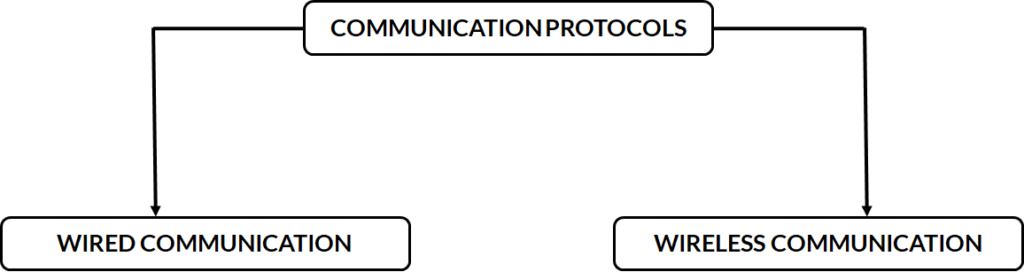
Wired Communication Protocol (major) :
UART – Universal Asynchronous Receiver & Transmitter
• Very Basic Communication Protocol.
• Full Duplex.
• Size of the data frame is limited to only 9 bits.
• Parity bit to allow for error checking.
• Cannot use multiple master systems and slaves.
• Baud rates of each UART must be within 10% of each other to prevent data loss.
• Low Speed.
• Less Distance.
• Cheap Cost.
SPI – Serial Peripheral Interface
• High Speed comparably UART.
• Full Duplex.
I2C – Inter Integrated Circuit
• Two Lines used. (SDA and SCL)
• SDA means Serial Data Line and SCL means Serial Clock Line.
• High Speed.
• Half Duplex.
Major used wireless communication protocols in IoT :

LPWAN
• LPWAN is a type of wide area network which connects devices over large area and allows long range communication at a lower bit rate, low cost and greater power efficiency.
• LPWAN supports a large number of devices over wide area in comparison to cellular services. Examples of LPWAN are NB-IoT, LoRa, SigFox etc
Why Zigbee?
• I am sure that you are familiar with short-range wireless networking technologies like Wi-Fi and Bluetooth which are used to connect devices. These technologies are fairly mainstream today and are used in specific use cases.
• For example, if you want to stream audio you likely to use Bluetooth likewise, if you are streaming video or large files, you are likely to use Wi-Fi.
• But let us think of a use case where we have to connect a large number of battery operated devices.
• Is it ok to operate using Wi-Fi or Bluetooth? The answer is clearly NO. Because Wi-Fi consumes a lot of power and is therefore not ideal for battery operated devices. Most of the Wi-Fi devices like your mobile phones or your laptop are usually changed on a daily basis.
• Then what about Bluetooth? You may say well. Bluetooth consumes less power than Wi-Fi so would that not be ideal for our use case? But you can connect only a limited number of devices to a Bluetooth network and therefore Bluetooth is not ideal for our use case as well.
• So, what could be a better solution to connect a large number of battery operated devices? ZigBee.
Zigbee
• Zigbee, like Wi-Fi and Bluetooth, is a short-range wireless protocol
• Long battery life.
• Low Cost.
• Data Rate: 250kbps.
• Range: 10 – 20 meters.(indoors)
• Security: 128bit AES algorithm to encrypt and authenticate.
• In fact the Swedish city Gothenburg is a giant zigbee network where over 250000 homes are connected together for the purpose of remote energy metering.
LoRa
We need a wireless network that consumes very low power, but also operates over distances larger than those of say, Wi-Fi. Is such a network even possible? Yes, That one is LoRa.
LoRa:
• LoRa – Long Range communication.
• Introduced by SEMTEC.
• Technology: Radio Modulation.
• Aim: Data transfer in low power and long range.
• Distance: 15 to 20km.
• Cellular based communication.
• LoRa Bit rate is quite Low. 10kb per second.
SigFox
• The IoT revolution is yet to reach its peak, but SigFox just announced that they aim for 1 billion devices connected to its network by 2023. so what is this technology? SigFox.
•This technology remotely interfaces battery operated devices and sensors to the internet.
• SigFox uses less power and is effective over long distances compared to connection protocols such as Bluetooth and Wi-Fi, which work best in the short range and use more power.
• Present in 72 countries & Regions.
• 2020 Range Covered: 5.7km.
• 0 to 140 message sent per device per day.
• Data Range: 100 to 600bps.
SigFox Work Flow:
• Objects — Base Station — SigFox Cloud — Internet, API and Call-backs.
NB-IoT
• NB-IoT or Narrow Band IoT is a standards based LPWAN that can be rolled out on top of the existing cellular network infrastructure.
• Cellular networks today allow us to transfer large volume of data at high speeds with low latency over very large distances.
• That trade off is that cellular devices consume a lot of power and are relatively expensive.
• No Gateway.
• NB-IoT operates via cellular carrier networks in one of the following 3 ways.
1. GSM Carrier.
2. LTE Channel.
3. Independent.
• IoT through cellular network.
• Data Rate: 20kbps – 5Mbps.
• Transmission Range: <35km.
 Sockerbruksgatan 7 53140 Lidköping
Sockerbruksgatan 7 53140 Lidköping kontakt@thingsatweb.se
kontakt@thingsatweb.se  +46 10 49 12000
+46 10 49 12000 




